Japanese & Korean Language Dataset
Home » Case Study » Japanese & Korean Language Dataset
Project Overview:
Objective
To embark on developing a comprehensive dataset encompassing Japanese and Korean languages, with the aim of facilitating advancements in machine translation, natural language processing, and linguistic research, it is imperative to meticulously strategize the collection process. Additionally, it is crucial to ensure the dataset’s inclusivity by incorporating diverse linguistic nuances and cultural expressions inherent to both Japanese and Korean languages. Furthermore, establishing robust validation methods and quality assurance protocols will be essential to guarantee the dataset’s reliability and accuracy. Moreover, fostering collaboration with language experts, native speakers, and researchers from diverse backgrounds will enrich the dataset’s content and enhance its utility across various applications.
Scope
Gather and annotate diverse textual data in both languages. Ensure the representation of various literary forms, including poetry, prose, and drama. Include colloquialisms, idiomatic expressions, and formal speech to capture the breadth of language usage. Moreover, incorporate a range of genres such as fiction, non-fiction, journalism, and academic writing. Additionally, consider including regional dialects and vernacular speech to showcase linguistic diversity. Furthermore, aim to cover a wide spectrum of topics to reflect the richness of human experience.
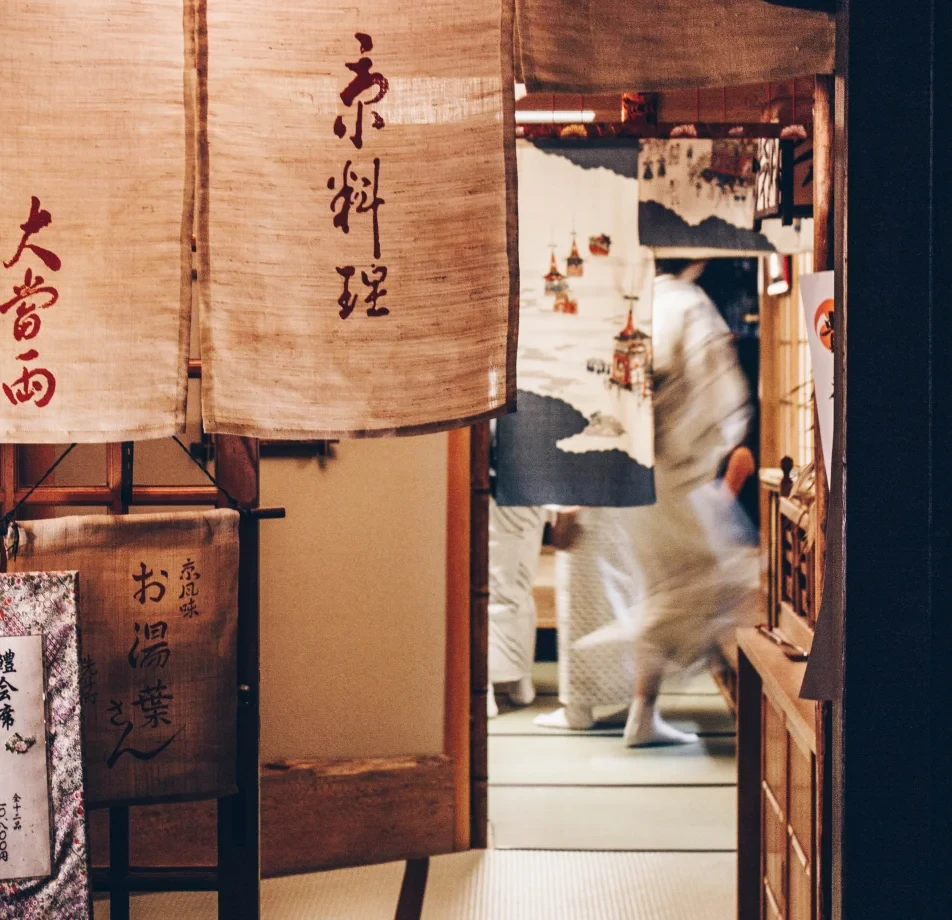




Sources
- News articles and reports: Collected and thoughtfully curated sources of information provide valuable insights into current events and issues. Additionally, they serve as essential tools for understanding complex topics and trends. Moreover, these sources often offer diverse perspectives, enabling readers to gain a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. Furthermore, they facilitate critical thinking by presenting facts, analysis, and commentary. Consequently, readers can make informed decisions based on a well-rounded understanding of the situation.
- Literary texts (novels, short stories, poetry): Carefully selected, thoughtfully curated, and comprising a diverse array of literary works.
- Online forums and social media platforms serve as virtual spaces where users can engage in discussions, share insights, and interact with one another. Transitioning into the realm of online interactions, individuals often express their opinions, ask questions, and seek advice from fellow users. Moreover, these platforms facilitate the exchange of information, fostering a sense of community among participants. Furthermore, users can explore diverse perspectives, broaden their knowledge, and engage in meaningful dialogue with others.
- Scientific journals and academic papers serve as rigorously collected and well-curated sources of scholarly information. Additionally, they offer a comprehensive array of insights into various fields of study. Moreover, these publications provide a platform for researchers to disseminate their findings and engage in scholarly discourse. Furthermore, they play a pivotal role in advancing knowledge and driving innovation within academia and beyond. Additionally, they undergo rigorous peer review processes to ensure the quality and reliability of the information they present.
- Conversational transcripts and dialogues: Meticulously gathered and thoughtfully compiled verbal exchanges.
- Business documents and formal emails: Carefully collected and professionally curated written communications.


Data Collection Metrics
- Total Data Points: 1,000,000
- Japanese: 500,000
- Korean: 500,000
- News Articles: 200,000 (100,000 each)
- Literary Texts: 150,000 (75,000 each)
- Online Forums: 200,000 (100,000 each)
- Academic Papers: 50,000 (25,000 each)
- Conversations: 200,000 (100,000 each)
- Business Documents: 200,000 (100,000 each)
Annotation Process
Stages
- Raw Data Cleaning: Exclusion of irrelevant, duplicate, or incomplete data.
- Segmentation: Decomposing texts into words or phrases.
- Part-of-Speech Tagging: Identifying word classes (verbs, nouns, etc.).
- Entity Recognition: Categorizing entities into person names, locations, etc.
- Sentiment Analysis: Labeling sentiment of sentences or paragraphs.
- Translation Pairing (for some texts): Pairing Japanese texts with their Korean equivalents and vice-versa for translation tasks.
Annotation Metrics
- Total Annotations: 5,000,000
- Segmented Tokens: 2,000,000
- Part-of-Speech Tags: 1,500,000
- Entity Tags: 1,000,000
- Sentiment Tags: 300,000
- Translation Pairs: 200,000




Quality Assurance
Stages
Expert Review: Additionally, linguistic experts in Japanese and Korean verify a subset of annotations.
Consistency Checks: Furthermore, automation tools detect potential inconsistencies.
Inter-annotator Agreement: Moreover, overlapping assignments ensure annotation consistency.
QA Metrics
- Annotations Reviewed by Experts: 500,000 (10% of total annotations)
- Inconsistencies Identified and Rectified: 40,000 (0.8% of total annotations)
Conclusion
The Japanese & Korean Language Dataset, through rigorous collection and annotation methodologies, establishes a robust foundation for diverse linguistic applications. Encompassing a wide spectrum of text forms and styles, this dataset is positioned to significantly aid advancements in East Asian linguistic computational tasks.

Quality Data Creation

Guaranteed TAT

ISO 9001:2015, ISO/IEC 27001:2013 Certified

HIPAA Compliance

GDPR Compliance

Compliance and Security
Let's Discuss your Data collection Requirement With Us
To get a detailed estimation of requirements please reach us.
