Geospatial Data Annotation for Mapping
Home » Case Study » Geospatial Data Annotation for Mapping
Project Overview:
Objective
Geospatial data annotation for mapping aims to improve map accuracy, support various applications, and address challenges in annotating geospatial data. Consequently, collaboration among professionals, technology developers, and data providers is essential to ensure continuous accuracy and accessibility in mapping.
Scope
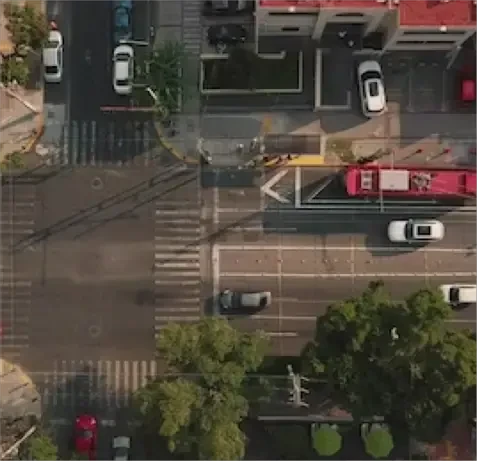
Geospatial Databases: By utilizing geospatial databases and archives, which contain spatial data, images, and other geographical information, you can significantly enhance your geographical analysis and decision-making processes.
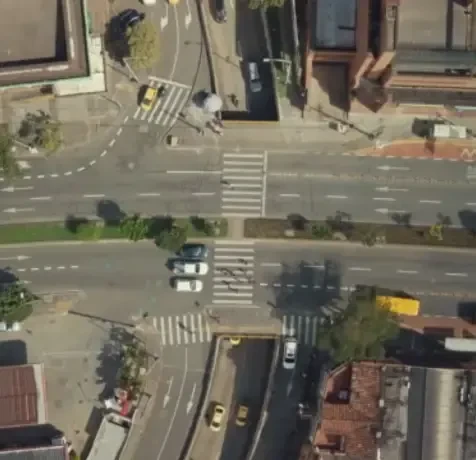
Annotation Tools: You can access geospatial data annotation tools and software, specifically designed for enhancing map accuracy and detail through precise annotation of spatial information.




Sources
- Geospatial Databases: By utilizing geospatial databases and archives, which contain spatial data, images, and other geographical information, you can significantly enhance your geographical analysis and decision-making processes.
- Annotation Tools: You can access geospatial data annotation tools and software, specifically designed for enhancing map accuracy and detail through precise annotation of spatial information.

Data Collection Metrics
- Data Volume: Total amount collected.
- Accuracy Rate: Precision of annotations for geographic features and coordinates.
Annotation Process
Stages
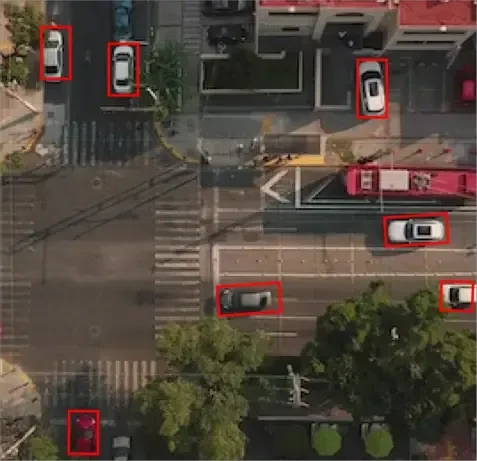
- Data Collection: Gather geospatial data, including maps, satellite images, and spatial information.
- Preprocessing: First, clean and prepare the data for annotation by addressing noise and inconsistencies. This step ensures that the data is ready for accurate annotation.
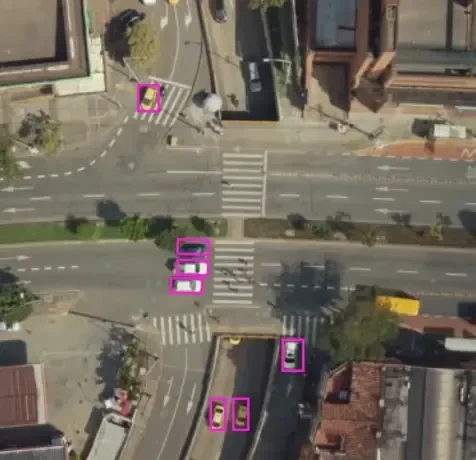
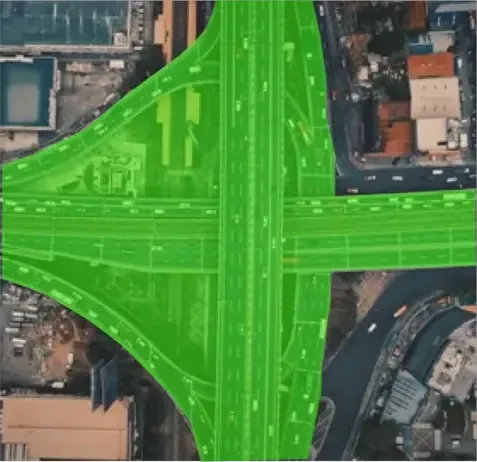
- Annotation Process: Next, annotate the geospatial data with precise details such as landmarks, roads, and boundaries. This step is crucial for creating detailed and useful maps.
- Quality Assurance: Then, review and validate the annotated data to ensure accuracy and completeness. This ensures that the final product meets high-quality standards.
- Data Integration: Afterward, integrate the annotated data into mapping systems to enhance map functionality. This step allows for the creation of more informative and reliable maps.
- Collaboration and Updates: Finally, collaborate with mapping professionals, developers, and data providers to ensure ongoing accuracy and updates in the geospatial information used for mapping. This continuous effort keeps the maps up-to-date and useful.
Annotation Metrics
- Inter-Annotator Agreement: Measure the level of consensus among different annotators to assess annotation reliability.
- Label Accuracy: Evaluate the precision and correctness of the annotations provided by the annotators.
- Feedback Mechanism: Finally, establish a feedback system to address uncertainties and continually enhance annotation quality.


Quality Assurance
Stages
Data Quality: To ensure the accuracy and reliability of collected data, it is essential to implement comprehensive data quality checks. For instance, validation rules can automatically detect and correct errors in data entries.
Privacy Protection: Strict adherence to privacy regulations is crucial. Firstly, always obtain informed consent from participants before collecting their data. Furthermore, anonymizing data protects participant identities wherever possible.
Data Security: To protect sensitive information, robust data security measures must be implemented. Firstly, using encryption safeguards data both at rest and in transit. Additionally, access controls restrict data access to authorized personnel only.
QA Metrics
- Data Accuracy: To ensure data accuracy, it is crucial to perform regular validation checks.
- Privacy Compliance: In addition, it is essential to regularly audit data handling processes for privacy compliance.
Conclusion
Geospatial data annotation is crucial for creating and maintaining accurate maps. As a result, it significantly improves spatial data precision and enables comprehensive mapping solutions for various applications. For example, it is essential for navigation, urban planning, disaster management, and environmental monitoring.

Quality Data Creation

Guaranteed TAT

ISO 9001:2015, ISO/IEC 27001:2013 Certified

HIPAA Compliance

GDPR Compliance

Compliance and Security
Let's Discuss your Data collection Requirement With Us
To get a detailed estimation of requirements please reach us.